The EU AI Act will soon go into effect, and it’s set to impact the financial industry the most. What can companies expect, and how can they achieve compliance before it’s too late?
What is the EU AI Act?
The EU AI Act is “a European regulation on artificial intelligence (AI)”, which dictates how businesses and organizations can safely use AI. It provides a framework that everything from small start-ups to giant corporations can use to “foster responsible artificial intelligence development and deployment in the EU”.
And it does this by defining its 3 TOP risk classifications, which organizations can use to evaluate their own AI systems, as well as the potential AI models and tools they want to implement in the future.
3 EU AI Act Risk Categories
- Unacceptable risk: Restrictive, manipulative, or discriminatory systems or apps (e.g., government-run social scoring of the type used in China);
- High risk: Tools that still serve a useful function but are susceptible to misuse, and are thus subject to strict obligations before market deployment (e.g., CV-scanning tool that ranks job applicants);
- Limited risk: All applications not explicitly banned or listed as high-risk; these are largely left unregulated.
High-Risk AI Systems in the Financial Industry
The EU AI Act sets the standard for the type of AI systems and models that all companies and organizations (in the EU or with EU data subjects) can use. That means the same rules that go for mega-tech corporations like Google and Meta also apply to your local mom-and-pop store (if Mom and Pop are tech-savvy enough to use AI tools).
However, financial services will be impacted the most by the EU AI Act. That’s because this industry most frequently relies on a multitude of models and data-driven processes, which are rapidly becoming faster and more accurate thanks to AI.
For example, the AI systems often used today by banks to determine an applicant’s creditworthiness will be considered High Risk when the AI Act goes into effect. And the same goes for the AI systems used in operating and maintaining financial infrastructure—many will soon rank as High Risk.
Examples of High-Risk AI Systems & Tools Frequently Used in Financial Services
AI Systems or Models that:
- Scan and evaluate CVs when ranking job applicants.
- Assess AI applications used for biometric identification.
- Categorize natural persons by credit score.
- Classify employment and employee management.
- Assess and set prices for life and health insurance (for natural persons).
- Make decisions affecting terms of work-related relationships, promotions, terminations, task allocation based on personal behaviour, etc.
- And many more.
Impact on Financial Service Providers
When striving to achieve EU AI Act compliance, the first step for any financial service provider is to assess their own AI system and see what risk classification it falls into. Luckily, the EU AI Act offers a quick and free way to do exactly that.
The Compliance Checker is an online form provided by the EU, which entities can use to evaluate their unique AI systems. By filling out the form, anyone can find out instantly where they stand and what next steps to take if the results read “High Risk” or (God forbid) “Unacceptable Risk”.
And it’s important to note that high-risk AI systems must pass a conformity assessment before being placed on the EU market, as evidenced by a “CE” marking, which indicates that the AI system represents compliance with EU legal standards.
Deployers of high-risk AI systems are subject to obligations that recognise the risks arising from their use of such AI systems. These obligations include complying with providers’ instructions for use and ensuring that the input data is transparent and suitable for the AI system’s intended purpose.
All participants in the AI deployment chain are subject to monitoring and reporting obligations concerning risks presented by high-risk AI systems.
Mitigate Risk with the AI Data Protector
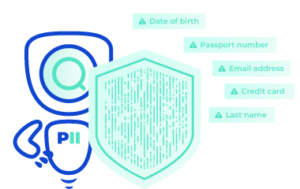
The whole purpose of the EU AI Act is to help companies and organizations eliminate or at least mitigate risk while still taking advantage of helpful AI tools. But you wouldn’t want these same tools to then interfere with your corporate data privacy or result in penalties and fines.
That’s where the AI Data Protector by PII Tools comes in. This is a PII detection API that automatically screens every file as it’s uploaded to your system. It then categorizes the results by risk assessment, allowing you to remediate any potentially at-risk data BEFORE feeding it to a third-party AI model.
The best part about the AI Data Protector is that it provides you with true automated data remediation. It does so by allowing you to auto-redact, encrypt, or quarantine any discovered sensitive data, preventing unauthorized exposure.
And since it’s self-hosted and secure, financial service providers can easily deploy the AI Data Protector within their own infrastructure. That way, no data ever leaves their environment, whether implemented within their own servers or on a private cloud.
Preparing for the EU AI Act
Financial institutions and service providers have a lot to do when getting ready for the EU AI Act. But the result of better security and protecting data subjects’ rights will be worth it in the end.
And the AI Data Protector will only make the preparations (and maintenance) that much easier. Plus, it will immediately improve your AI system’s risk classification under the EU AI Act, allowing you to eliminate potential harm and still get the most out of any time-saving, morale-boosting AI tools!
Financial Services Are Impacted the Most by the EU AI Act. Get Ready with the AI Data Protector!